Sociology 182: Urban Problems C. Chase-Dunn
Spring, 2005 Sproul
1102
Tu Thurs 8:10 to 9:30
(v.3/29/05)
This course is about the
emergence of sedentism, the invention of towns and cities, the interactions between
sedentary and nomadic peoples, and the institutional responses to the problems
created when humans reside close to one another. Topics covered are: hamlets,
settlement systems, ancient cities, and the interactions of city and country.
We will also study industrial urbanization, megacities and the urbanization of
the global system with its world cities tightly linked by communications,
transportation, trade and organization. Contemporary urban issues in Southern
California and other regions will also be considered. The course will employ
the comparative world-systems perspective to examine urban problems since the
invention of sedentism.

urban heat island effect
This is primarily a
reading and lecture course. Assigned readings should be completed by the date
under which they appear. Readings marked with an asterisk (*) are required.
Others are recommended. Grading is based on the midterm (30%), the final (30%),
the term
paper (25%) and attendance (15%).
Course
Web Site is at: http://iLearn.ucr.edu/ A student's username
is the same as the student's user account on the server student.ucr.edu. The
student's password is his or her 9-digit social security number with no dashes
or spaces.
The following books are available at the University Book
Store and are on reserve:
Mark Abrahamson, Global
Cities
Peter J. Taylor, World
City Network
Available at the
University Photocopy Service is a reader for the course entitled Urban Problems
Reader.
March 29: Overview of course.
March 31 the comparative world-systems perspective
*C. Chase-Dunn and T.D.
Hall, “Global social
change in the long run” (in Urban Problems Reader)
April 5 From nomadism to sedentism: camps, hamlets, towns
C. Chase-Dunn, “The role of
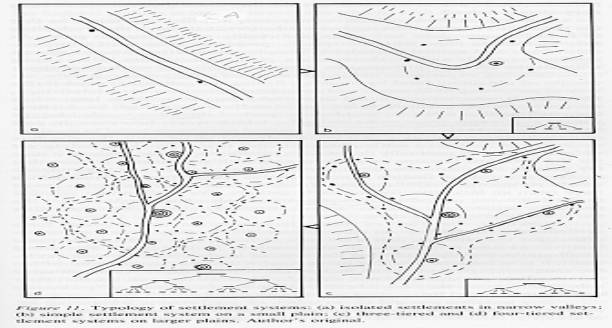
ecosettlement systems in social evolution” in Urban Problems Reader, up
to but not including the section on “settlement size hierarchies.”
April 7 : Settlement Size Hierarchies
* C. Chase-Dunn, “The role of
ecosettlement systems in social evolution” in Urban Problems Reader, read
the section on “settlement size hierarchies”
The settlement systems of
complex chiefdoms
Patrick Kirch, The
Evolution of Polynesian Chiefdoms
David G. Anderson, The
Savannah River Chiefdoms
April 12 The emergence of cities
* Christopher Chase-Dunn,
Daniel Pasciuti, Alexis Alvarez and Thomas D. Hall “ The
ancient Mesopotamian and Egyptian world-systems”
Guillermo Algaze, The
Uruk World-System
Kasja Ekholm-Friedman,
“On the evolution of global systems, part 1: the Mesopotamian heartland” Pp.
153-168 in Robert A. Denemark et al (eds.) World System History
(Routledge 2000).
April 14 Cities and Empires Term Paper Outline Due ,
Midterm Study
Questions Handed Out
* Christopher Chase-Dunn,
Alexis Alvarez and Daniel Pasciuti, “Power and size:
urbanization and empire formation in world-systems”
Thomas Barfield, The
Perilous Frontier
Frederick J. Teggart, Rome
and China
April 19 Cities in the Afroeurasian System
* Christopher Chase-Dunn
and E. Susan Manning, “City
systems and world-systems: Four millennia of city growth and decline’
Janet Abu-Lughod, Before
European Hegemony
C. Chase-Dunn and T.D.
Hall, Rise and Demise (Westview 1996) Chapter 8
April 21 Midterm
April 26 Cities in the Modern World-System
* C. Chase-Dunn, “The role of
ecosettlement systems in social evolution” in Urban Problems Reader, read
from the section on “the volcano model” to the end.
Abel Wolman, “The
metabolism of cities.” Science 1965
Kenneth Boulding, “The
city as an element in the international system.” Daedalus: Journal of
the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, Fall, 1968.
Charles Tilly, Coercion,
Capital, and European states, AD 990-1990 (Blackwell, 1990)
April 28 Cities and Globalization
* Mark Abrahamson, Global
Cities, Chapters 1-3
Saskia Sassen, The
Global City: New York, London, Tokyo.
May
3 Cities and Globalization
* Mark Abrahamson, Global
Cities, Chapters 4-6
Smith, David A. and
Michael Timberlake 1995 “Conceptualizing and mapping the structure of the world
system’s city system,” Urban Studies
32,2:287-302.
May
5 Cities and Globalization
* Mark Abrahamson, Global
Cities, Chapters 7-8
May 10 The World City Network
* Peter J. Taylor, The
World City Network, Prologue and Chapter1
May 12 The World City Network
* Peter J. Taylor, The
World City Network, Chapters 2-4
May 17 The World City Network
* Peter J. Taylor, The
World City Network, Chapters 5-7
May 19 The World City Network
* Peter J. Taylor, The
World City Network, Chapters 8-9
Who Rules Socal?
Allen J. Scott and Edward Soja, The City: Los Angeles and Urban
Theory
Low density and multicentric cities
Mixed Use Developments
Global Impasse
June 2 Lyrical Upsurge
* Christopher Chase-Dunn
and Terry Boswell, “Global
democracy: a world-systems perspective”
June 6, 3-5 pm Final Exam