rise, fall and upward sweeps:
the emergence of a global state*

Department of Sociology and Institute for Research on World-Systems
University of California-Riverside
*Thanks
to E. N. Anderson and Peter Turchin for their contributions to ideas developed
below.
This is the outline for an interactive teleconference on Human Sciences and Complexity, a 4-campus interdisciplinary project that includes
scholars from UC-Irvine, UCLA, UC-San Diego and UCR. It is based on research proposal that is being supported by the U.S.
National Science Foundation’s program on Human Social Dynamics. That proposal is available at
https://irows.ucr.edu/research/citemp/globstat/globstatprop.htm.
The time of the interactive teleconference is from 2 to 3:05 on
Friday,
October 14 ,and the UCR location will be in Olmsted 1208. An earlier version of
this lecture presented at the University of Victoria
Is
available at https://irows.ucr.edu/cd/lectures/lecturestoc.htm
The comparative world-systems perspective: systems of societies as the unit of analysis for explaining cultural evolution.
Core/periphery hierarchies
Semiperipheral development
World-systems: small, medium and large. Bounding premodern world-systems. Important interaction networks
Waves of network expansion and contraction (pulsation and eventual globalization)
Expansion of the central system and incorporation of other
regional systems
Polities: bands, tribes, chiefdoms, states, empires
The iteration model (not time today). See https://irows.ucr.edu/papers/irows20/irows20.htm
Rise and fall and upward sweeps of hierarchy formation
Semiperipheral marcher chiefdoms
Semiperipheral marcher states
Semiperipheral capitalist city-states
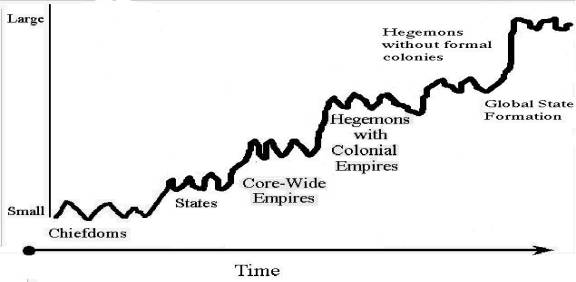
Rise
and Fall with Upward Sweeps of Polity Size
Modeling agrarian empires. Two-level models. States and interstate systems. Endogenous to what?
Modeling thallasocratic capitalist city-states
From core-wide empires created by tributary marcher states to colonial empires and a multicentric core with a hegemon.
Waves of colonization and decolonization: global polity formation
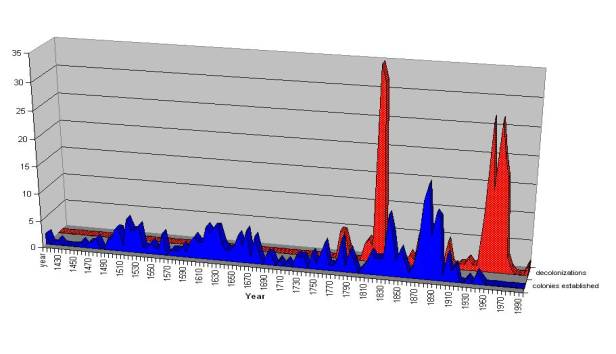
Waves of colonization and decolonization based on
Henige (1970)
Types of international political integration:
A peaceful system of sovereign states
A confederation of states
A real global state with the power to outlaw warfare and to enforce the law
Global democracy
Bibliography
Abu-Lughod, Janet Lippman 1989 Before European
Hegemony: The World System A.D.
1250-1350 New York: Oxford University Press.
Anderson, David G. 1994 The
Savannah River Chiefdoms. Tuscaloosa: University of Alabama Press.
Arrighi, Giovanni 1994 The Long Twentieth
Century: Money, Power and the Origins of
Our
Times.
London: Verso
Bairoch, Paul 1988 Cities and Economic
Development. Chicago: University of
Chicago
Press.
Barabási, A.-L. 2002. Linked: The New Science of
Networks. Cambridge, MA: Perseus Publishing.
Barfield, Thomas J. 1989. The Perilous Frontier:
Nomadic Empires and China.
Cambridge, MA: Basil
Blackwell.
Bentley, Jerry H. 1993.
Old World Encounters:
Cross-Cultural Contacts and Exchanges in Pre-Modern
Times.
Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Bergesen,
Albert and Ronald Schoenberg 1980 “Long waves of colonial expansion and
contraction
1415-1969” Pp. 231-278 in Albert Bergesen (ed.) Studies of the Modern
World-System. New York: Academic
Press
Boli, John and George M. Thomas 1997 “World culture
in the world polity,” American
Sociological Review 62,2:171-190 (April).
__________ (eds.)1999 Constructing World Culture: International Nongovernmental Organizations
Since
1875. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Boserup, Ester1981. Population and Technological
Change. Chicago: University of Chicago
Press.
Braudel, Fernand 1979 The Perspective of the
World. New York: Harper and Row.
Carneiro, Robert L. 1978 “Political expansion as an
expression of the principle of
competitive exclusion,”
Pp. 205-223 in Ronald Cohen and Elman R. Service
(eds.) Origins of the State: The Anthropology of
Political Evolution. Philadelphia:
Institute
for the Study of Human Issues.
________ 2004 “The political unification of the
world: whether, when and how – some
speculations.” Cross-Cultural
Research 38,2:162-177 (May).
Chandler, Tertius 1987 Four Thousand Years of
Urban Growth. Edwin Mellen Press:
Lewiston/Queenston,
Lampeter.
Christopher
Chase-Dunn. 1990 "World state formation: historical processes and
emergent necessity" Political Geography
Quarterly, 9,2: 108-30 (April).
https://irows.ucr.edu/papers/irows1.txt
Chase-Dunn, Christopher and Thomas D. Hall. 1997 Rise and Demise:Comparing
World-Systems Boulder, CO.: Westview
Chase-Dunn,
C. and E. Susan Manning 2002 “City systems and world-systems: four
millennia of city growth an decline.” Cross-Cultural
Research 36,4:379-398.
Chase-Dunn, Christopher, Yukio Kawano and Benjamin
Brewer 2000 “Trade
globalization since
1795: waves of integration in the world-system.”
American Sociological
Review,
February.
Chase-Dunn,
Christopher, Andrew Jorgenson, Thomas E. Reifer and Shoon Lio Forthcoming. “The
trajectory of the United States in the world-system,” Sociological
Perspectives.
Christian,
David 2004 Maps of Time. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Cioffi-Revilla, Claudio 1996 “Origins and Evolution of War and Politics,”International Studies Quarterly, Vol. 40, no. 1, March pp. 1-4.
Collins,
Randall 1999 Macrohistory: Essays in the Sociology of the Long Run.
Stanford, CA:
Stanford
University Press
Denemark, Robert,
Jonathan Friedman, Barry K. Gills and George Modelski (eds.) 2000
World System History: the social science of long-term
change. London:
Routledge.
Diamond, Jared 2004 Collapse.
New York: Viking
Fischer,
David Hackett 1996 The Great Wave: Price Revolutions and the Rhythm of
History. New York: Oxford
University Press.
Frank,
Andre Gunder and Barry K. Gills (eds.) 1993 The World System: Five Hundred
Years or Five Thousand ? London: Routledge.
Review 15:3(Sum):335-72.
Friedman, Jonathan and
Michael Rowlands 1977 "Toward an epigenetic model of the
evolution of 'civilization.'"
Pp. 201-78 in J. Friedman and M. Rowlands (eds.)
The Evolution of Social Systems. London:Duckworth.
Galloway,
Patrick R. 1986 “Long-term fluctuations in climate and population in the
preindustrial era.” Population and Development
Review 12,1:1-24 (March).
Goldfrank,
Walter L. 1999 “Beyond hegemony” in Volker Bornschier and Christopher
Chase-Dunn (eds.) The Future of Global Conflict. London:
Sage.
Gimblett,
Randy 2001 Integrating Geographic Information Systems and Agent-Based
Modeling:
Techniques for Simulating Social and Ecological Processes New
York: Oxford University Press.
Goldstone, J. A. 1991. Revolution and rebellion in
the Early Modern world. University of
California Press, Berkeley, CA.
Graber, Robert Bates 2004 “Is a world state just a
matter of time?: a population-pressure
alternative.” Cross-Cultural Research 38,2:147-161 (may).
Hanneman,
Robert A. 1988-89 Computer Assisted Theory Building. Beverly Hills: Sage.
_________1995
"Discovering Theory Dynamics by Computer Simulation:
Experiments on State Legitimacy and Capitalist
Imperialism." Pp. 1-46 in Peter
Marsden (ed.) Sociological Methodology (with
Randall Collins and Gabrielle
Mordt).
Hardt, Michael and Antonio Negri 2004 Multitude. New York: Penguin
Harris, Marvin. 1977.
Cannibals and Kings: The Origins of Cultures. New York:
Random House.
Henige, David P. 1970 Colonial
Governors from the Fifteenth Century to the Present. Madison, WI.:
University of Wisconsin
Press.
Hughes, Barry B. 1996 International Futures:
Choices in the Creation of a New World
Order. Boulder, CO:Westview.
Jervis, Robert 1985 "From Balance to Concert:
A Study in International Security
Cooperation," World
Politics 38,1:
58-79
Johnson, Allen W. and Timothy Earle. 1987. The
Evolution of Human Societies: From
Foraging Group to
Agrarian State. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Johnson, Amber Lynn 2004 “ Why not to expect a
“world state.” Cross-Cultural Research
38,2: 119-132 (May).
Khaldun, Ibn 1981 The
Muqaddimah. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Kirch, Patrick V. 1984 The
Evolution of Polynesian Chiefdoms. Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press.
_________ 1991
“Chiefship and competitive involution: the Marquesas Islands of Eastern
Polynesia” Pp. 119-145
in Timothy Earle (ed.) Chiefdoms: Power, Economy and Ideology.
Cambrdige: Cambridge
University Press.
Kowalewski, David and Dean Hoover 1995 “The future
world-system: a dynamic model”
World Futures 44:263-285.
Larsen, Mogens T. 1976 The Old Assyrian City
State and Its Colonies. Copenhagen: Akademisk Forlag.
Lattimore, Owen. 1940. Inner Asian Frontiers of
China. New York: American
Geographical Society, republished 1951, 2nd
ed. Boston: Beacon Press.
Lenski, Gerhard 2005 Ecological-Evolutionary
Theory. Boulder, CO: Paradigm.
Levy, Jack S. and William R. Thompson 2005 The
Evolution of War. Englewood Cliffs, NY: Prentice-Hall.
Li, B. L. and E. L. Charnov. 2001.
Diversity-stability relationships revisited: scaling rules for
biological communities
near equilibrium. Ecological Modelling, 140: 247-254.
Marano, Louis A 1973 “A
macrohistoric trend toward world government.” Behavior
Science Notes 8,1, 35-39
Mann, Michael.
1986. The sources of social
power: Volume I: A history of power from
the beginning to a.d.
1760. Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press.
McNeill, J.R. and
William McNeill 2003 The Human Web. New York: Norton
Modelski, George 2003 World
Cities: –3000 to 2000. Washington, DC: Faros 2000
Modelski,
G., W. R. Thompson. 1996. Leading sectors and world powers: the co-evolution
of
global politics and economics. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia,
SC.
Murphy, Craig 1994 International Organization and Industrial
Change: Global Governance
since 1850. New York: Oxford.
Naroll, Raul 1967
“Imperial cycles and world order,” Peace Research Society: Papers, VII,
Chicago Conference,
1967: 83-101.
O’Rourke, Kevin H and Jeffrey
G. Williamson 1999 Globalization and History: The Evolution
of a 19th
Century Atlantic Economy. Cambridge, MA.: MIT Press.
Pasciuti, Daniel and
Christopher Chase-Dunn 2002 “Estimating the population sizes of
cities.” https://irows.ucr.edu/research/citemp/estcit/estcit.htm
Peregrine, Peter N.,
Melvin Ember and Carol R. Ember 2004 “Predicting the future state
of the world using
archaeological data: an exercise in archaeomancy.” Cross-
Cultural Research 38,2: 133-146 (may).
Polanyi, Karl. 1944. The Great Transformation:
The Political and Economic Origins of
Our Time. Boston: Beacon Press.
_____. 1957. "Aristotle Discovers the
Economy." Pp. 64-96 in Trade and Market in the
Early Empires, edited by Karl
Polanyi, Conrad M. Arensberg, and Harry W.
Pearson. Chicago:
Regnery.
Robinson, William I. 2004 A Theory of Global
Capitalism. Baltimore: MD. Johns Hopkins
University Press.
Roscoe, Paul 2004 “The
problems with polities: some problems in forecasting global political
integration.” Cross-Cultural Research 38,2:102-11.
Rummel, R. J. 2002.
url: http://www.hawaii.edu/powerkills/LINKS.HTM#freedom -
Link to Cross-National
Data/Statistics
Redman, Charles L. 1999 Human Impact on Ancient Environments.
Tucson: University
of Arizona Press.
Sachs, Jeffrey 2005 The
End of Poverty. New York: Penguin.
Sanderson, Stephen K.
1990 Social Evolutionism. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell.
Sassen, Saskia. 1991. Global Cities. Princeton: Princeton
University Press.
Silver, Beverly 2003 Forces
of Labor. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sklair, Leslie. 2001. The Transnational Capitalist Class.
Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
Smith, D., and D. R.
White. 1992.Structure and Dynamics of the Global Economy:
Network Analysis of
International Trade 1965-1980. Social Forces 70:857-894.
Spufford, P. 2002,
Power and Profit: The Merchant in Medieval Europe. London & NY:
Thames & Hudson.
Taagepera, Rein 1978
"Size and duration of empires: growth-decline curves, 3000
to
600 BC" Social Science Research 7:180-196
________ 1997 “Expansion and contraction patterns
of large polities: context for
Russia.” International
Studies Quarterly 41,3: 475-504.
Taylor, Peter J. 1996 The Way the Modern World
Works: World Hegemony to World
Impasse
. New
York: John Wiley.
Teggart, Frederick J. 1939. Rome and China: A
Study of Correlations in Historical
Events. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Tilly, Charles 1990 Coercion, Capital and
European States: AD 990-1990. Cambridge,
MA: Blackwell.
Tobler, Waldo and S. Wineburg 1971 “A Cappadocian
Speculation” Nature 231, May 7.
Turchin, P. 2003. Historical
dynamics: why states rise and fall. Princeton University Press,
Princeton, NJ.
Turchin, P., and T. D.
Hall. 2003. Spatial synchrony among and within world-systems:
insights from
theoretical ecology. Journal of World Systems Research 9,1
http://csf.colorado.edu/jwsr/archive/vol9/number1/pdf/jwsr-v9n1-turchinhall.pdf
Thompson, William R. 1990 "Long waves,
technological innovation and relative
decline." International
Organization 44:201-33.
________________ (ed.) 2001 Evolutionary
Interpretations of World Politics. London: Routledge.
Van der Pijl, Kees. 1984. The Making of an Atlantic Ruling Class. London: Verso.
Wallerstein, Immanuel. 1984. “The three
instances of hegemony in the history of the
capitalist
world-economy.” Pp. 100-108 in Gerhard
Lenski (ed.) Current Issues and Research in
Macrosociology, International Studies in Sociology and
Social Anthropology,
Vol. 37. Leiden: E.J. Brill.
________________
2000 The Essential
Wallerstein. New York: New Press.
Wendt, Alex 2003 “Why a world state is inevitable” European
Journal of International Relations.
9,4: 491-542.
White, Douglas R., F. Harary. 2001 “The
Cohesiveness of Blocks in Social Networks:
Node
Connectivity and Conditional Density.” Sociological Methodology 2001,
vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 305-359. Blackwell Publishers, Inc., Boston, USA and
Oxford, UK.
Wilkinson, David. 1987 "Central
civilization" Comparative Civilizations Review 17:31-
59 (Fall).
_________ 1991 “Core, peripheries and
civilizations,” Pp. 113-166 in C. Chase-Dunn
and T.D. Hall (eds.) Core/Periphery Relations in
Precapitalist Worlds. Boulder, CO:
Westview Press
_________2004 “The power configuration of the
central world-system, 1500-700 BC”
Journal of World-Systems Research 10,3: 655-720.